African American Literature Themes
African American Literature Themes. The thematic richness of African American literature extends far beyond its historical roots, continually adapting to reflect the evolving challenges, triumphs, and nuances of Black life in America. Its themes not only capture the personal and communal dimensions of African American identity but also engage with the broader struggles of humanity, making it a critical component of global literature.The Interconnectedness of Themes in African American Literature
A remarkable feature of African American literature is how its themes often intersect and reinforce one another. For instance, the struggle for identity is deeply entwined with the impacts of racism and social injustice, as the pervasive effects of systemic discrimination shape how African Americans perceive themselves and are perceived by others. The theme of community and family often provides a counterbalance, serving as a sanctuary and source of strength in navigating these challenges. The celebration of cultural heritage further enriches these themes, offering a lens through which authors critique the erasure of Black identity while honoring the resilience of African traditions. These intersections create a multilayered narrative structure, allowing writers to address complex issues holistically. This interconnectedness ensures that the literature resonates deeply with readers, offering both personal relatability and a broader social commentary.
The celebration of cultural heritage further enriches these themes, offering a lens through which authors critique the erasure of Black identity while honoring the resilience of African traditions. These intersections create a multilayered narrative structure, allowing writers to address complex issues holistically. This interconnectedness ensures that the literature resonates deeply with readers, offering both personal relatability and a broader social commentary.
Expanding the Theme of Identity: A Multifaceted Journey
The exploration of identity in African American literature often delves into the tension between individuality and collective experience. Writers like Ralph Ellison in *Invisible Man* explore the alienation that arises when one's identity is overlooked or diminished by societal forces. This struggle is not merely an internal conflict but a direct response to the external pressures of racism, stereotyping, and systemic marginalization. Furthermore, African American literature frequently interrogates the concept of double consciousness, a term coined by W.E.B. Du Bois to describe the dual awareness experienced by African Americans as they navigate their identities in a racially stratified society. This theme extends into contemporary works that examine intersectionality, exploring how overlapping aspects of identity—such as gender, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status—shape individual experiences. Authors like Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie and Jacqueline Woodson highlight how these layers of identity interact, creating complex characters that defy simplistic categorization.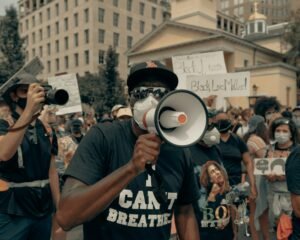
Racism and Social Injustice: A Mirror and a Catalyst for Change
The themes of racism and social injustice in African American literature remain as urgent today as they were during the abolitionist and Civil Rights eras. These themes serve both as a mirror to reflect the realities of Black life and as a catalyst to inspire action. Through vivid depictions of systemic oppression, authors force readers to confront the moral and ethical failings of society. Contemporary works like Angie Thomas's *The Hate U Give* and Colson Whitehead's *The Nickel Boys* bring these themes into the modern era, addressing police brutality, mass incarceration, and the lingering effects of historical injustices. By centering the lived experiences of African Americans, these works not only document societal failings but also humanize their impact, fostering empathy and understanding. Moreover, these themes extend beyond the individual, interrogating institutional power structures that perpetuate inequality. Writers often use their works as platforms to advocate for systemic change, blending artistry with activism. By doing so, African American literature transforms from a mere reflection of society to a powerful tool for reimagining it.The Role of Memory and Trauma in African American Literature Themes
Memory and trauma are recurring themes in African American literature, shaping narratives that seek to preserve history and process collective pain. Authors like Toni Morrison and Octavia Butler use memory as both a storytelling device and a means of resistance, reclaiming narratives that have been ignored or suppressed. These themes often address the intergenerational transmission of trauma, exploring how the scars of slavery, segregation, and systemic racism continue to affect descendants. Morrison's *Beloved*, for example, illustrates how memory can be both a source of pain and a pathway to healing. Through the character of Sethe, Morrison delves into the lingering impact of slavery, showing how personal and collective histories are intertwined. Similarly, Butler’s speculative fiction uses futuristic and fantastical settings to confront historical trauma, bridging the past and future to offer new perspectives on resilience and survival. Cultural Heritage: A Celebration and a Challenge
The celebration of cultural heritage is a central theme in African American literature, offering both a foundation for identity and a means of resistance against cultural erasure. Folklore, music, and oral traditions are frequently woven into narratives, connecting contemporary characters to their ancestral roots. These elements not only celebrate African heritage but also challenge the dominant narratives that have sought to marginalize Black culture.
In works like Zora Neale Hurston’s *Their Eyes Were Watching God* and Alice Walker’s *The Color Purple*, the use of dialect, storytelling, and cultural references highlights the richness of African American traditions. By incorporating these elements, authors assert the importance of cultural pride and continuity, even in the face of oppression.
Additionally, modern authors like Ta-Nehisi Coates and Yaa Gyasi expand on this theme by exploring the diasporic connections between African Americans and their ancestral homelands. This global perspective broadens the thematic scope of African American literature, emphasizing the interconnectedness of Black experiences across the world.
Resilience and Hope: The Heart of African American Literature Themes
At the core of African American literature is a profound sense of resilience and hope. Despite the weight of the themes it addresses, the literature often carries an undercurrent of optimism and possibility. This resilience is reflected in characters who overcome adversity, communities that thrive despite systemic challenges, and narratives that envision a better future.
Hope is a recurring thread, from the spirituals sung by enslaved individuals to the empowering speeches and writings of Civil Rights leaders. This sense of hope inspires readers to believe in the possibility of change, encouraging them to confront injustices and envision a world where equality and justice prevail.
Frequently Asked Questions About African American Literature Themes
1. What are the primary themes in African American literature?
The primary themes include identity, racism and social injustice, resilience, community and family, cultural heritage, liberation, and spirituality.
2. How does African American literature address the theme of identity?
It explores the quest for self-definition, the impact of systemic racism, and the interplay of individual and collective experiences in shaping identity.
3. What role does racism play in African American literature themes?
Racism is a central theme, often depicted through systemic oppression, personal discrimination, and its psychological and social consequences.
4. Why is the theme of resilience important in African American literature?
Resilience highlights the ability of individuals and communities to endure and overcome adversity, reflecting strength and hope.
5. How do authors incorporate cultural heritage into African American literature themes?
They weave in folklore, oral traditions, music, dialects, and ancestral references to celebrate and preserve cultural identity.
6. What is double consciousness, and how does it relate to African American literature?
Double consciousness, introduced by W.E.B. Du Bois, describes the dual awareness of being African and American, a recurring theme in African American literature.
7. How do African American writers explore the impact of social injustice?
They depict characters navigating systemic inequality, revealing its effects on their lives and advocating for change through their narratives.
8. What role do family and community play in African American literature themes?
Family and community are portrayed as sources of strength, support, and identity, often helping characters navigate societal challenges.
9. How has African American literature evolved over time?
It has grown from early narratives of enslavement to include diverse genres and themes that reflect contemporary issues and experiences.
10. What is the significance of spirituality in African American literature?
Spirituality provides a means of coping, resilience, and hope, often interwoven with themes of redemption and liberation.
11. How do African American authors address intersectionality in their works?
They explore how race intersects with gender, class, and sexuality to create complex and multifaceted characters and narratives.
12. Why is memory and trauma a recurring theme in African American literature?
These themes address the legacy of slavery and systemic oppression, exploring how historical pain shapes individual and collective identities.
13. How do African American writers use literature as a tool for activism?
Through vivid storytelling and compelling themes, authors challenge societal norms, advocate for justice, and inspire change.
14. What influence has the Harlem Renaissance had on African American literature themes?
The Harlem Renaissance emphasized themes of cultural pride, artistic expression, and racial identity, setting the stage for modern African American literature.
15. How do contemporary authors expand on traditional African American literature themes?
They tackle modern issues like police brutality, climate justice, and mental health while staying rooted in the historical and cultural foundations of the genre.
Conclusion: The Timeless Relevance of African American Literature Themes
The themes of African American literature are as relevant today as they were when the first narratives emerged from the shadows of slavery. They speak to the enduring struggles for freedom, equality, and recognition while celebrating the creativity, resilience, and strength of African American voices. These themes provide a roadmap for understanding the complexities of race, identity, and culture, offering insights that are invaluable in today’s increasingly interconnected world.
As new generations of writers continue to expand and reinterpret these themes, African American literature remains a vibrant and evolving tradition. Its stories inspire, educate, and challenge, ensuring that the voices of the past and present continue to shape the future. Through these enduring themes, African American literature solidifies its place as a cornerstone of global literary and cultural discourse.
Cultural Heritage: A Celebration and a Challenge
The celebration of cultural heritage is a central theme in African American literature, offering both a foundation for identity and a means of resistance against cultural erasure. Folklore, music, and oral traditions are frequently woven into narratives, connecting contemporary characters to their ancestral roots. These elements not only celebrate African heritage but also challenge the dominant narratives that have sought to marginalize Black culture.
In works like Zora Neale Hurston’s *Their Eyes Were Watching God* and Alice Walker’s *The Color Purple*, the use of dialect, storytelling, and cultural references highlights the richness of African American traditions. By incorporating these elements, authors assert the importance of cultural pride and continuity, even in the face of oppression.
Additionally, modern authors like Ta-Nehisi Coates and Yaa Gyasi expand on this theme by exploring the diasporic connections between African Americans and their ancestral homelands. This global perspective broadens the thematic scope of African American literature, emphasizing the interconnectedness of Black experiences across the world.
Resilience and Hope: The Heart of African American Literature Themes
At the core of African American literature is a profound sense of resilience and hope. Despite the weight of the themes it addresses, the literature often carries an undercurrent of optimism and possibility. This resilience is reflected in characters who overcome adversity, communities that thrive despite systemic challenges, and narratives that envision a better future.
Hope is a recurring thread, from the spirituals sung by enslaved individuals to the empowering speeches and writings of Civil Rights leaders. This sense of hope inspires readers to believe in the possibility of change, encouraging them to confront injustices and envision a world where equality and justice prevail.
Frequently Asked Questions About African American Literature Themes
1. What are the primary themes in African American literature?
The primary themes include identity, racism and social injustice, resilience, community and family, cultural heritage, liberation, and spirituality.
2. How does African American literature address the theme of identity?
It explores the quest for self-definition, the impact of systemic racism, and the interplay of individual and collective experiences in shaping identity.
3. What role does racism play in African American literature themes?
Racism is a central theme, often depicted through systemic oppression, personal discrimination, and its psychological and social consequences.
4. Why is the theme of resilience important in African American literature?
Resilience highlights the ability of individuals and communities to endure and overcome adversity, reflecting strength and hope.
5. How do authors incorporate cultural heritage into African American literature themes?
They weave in folklore, oral traditions, music, dialects, and ancestral references to celebrate and preserve cultural identity.
6. What is double consciousness, and how does it relate to African American literature?
Double consciousness, introduced by W.E.B. Du Bois, describes the dual awareness of being African and American, a recurring theme in African American literature.
7. How do African American writers explore the impact of social injustice?
They depict characters navigating systemic inequality, revealing its effects on their lives and advocating for change through their narratives.
8. What role do family and community play in African American literature themes?
Family and community are portrayed as sources of strength, support, and identity, often helping characters navigate societal challenges.
9. How has African American literature evolved over time?
It has grown from early narratives of enslavement to include diverse genres and themes that reflect contemporary issues and experiences.
10. What is the significance of spirituality in African American literature?
Spirituality provides a means of coping, resilience, and hope, often interwoven with themes of redemption and liberation.
11. How do African American authors address intersectionality in their works?
They explore how race intersects with gender, class, and sexuality to create complex and multifaceted characters and narratives.
12. Why is memory and trauma a recurring theme in African American literature?
These themes address the legacy of slavery and systemic oppression, exploring how historical pain shapes individual and collective identities.
13. How do African American writers use literature as a tool for activism?
Through vivid storytelling and compelling themes, authors challenge societal norms, advocate for justice, and inspire change.
14. What influence has the Harlem Renaissance had on African American literature themes?
The Harlem Renaissance emphasized themes of cultural pride, artistic expression, and racial identity, setting the stage for modern African American literature.
15. How do contemporary authors expand on traditional African American literature themes?
They tackle modern issues like police brutality, climate justice, and mental health while staying rooted in the historical and cultural foundations of the genre.
Conclusion: The Timeless Relevance of African American Literature Themes
The themes of African American literature are as relevant today as they were when the first narratives emerged from the shadows of slavery. They speak to the enduring struggles for freedom, equality, and recognition while celebrating the creativity, resilience, and strength of African American voices. These themes provide a roadmap for understanding the complexities of race, identity, and culture, offering insights that are invaluable in today’s increasingly interconnected world.
As new generations of writers continue to expand and reinterpret these themes, African American literature remains a vibrant and evolving tradition. Its stories inspire, educate, and challenge, ensuring that the voices of the past and present continue to shape the future. Through these enduring themes, African American literature solidifies its place as a cornerstone of global literary and cultural discourse.https://howtoplaythedjembedrums.com/african-american-literature-themes/






 FAQs About African Grey Parrot Price and Ownership
1. How much does an African grey parrot cost?
The African grey parrot price typically ranges from $1,000 to $3,500 depending on the
FAQs About African Grey Parrot Price and Ownership
1. How much does an African grey parrot cost?
The African grey parrot price typically ranges from $1,000 to $3,500 depending on the  3. Libya
- Known for its vast oil reserves.
- Features the Sahara Desert and Roman ruins like Leptis Magna.
4.
3. Libya
- Known for its vast oil reserves.
- Features the Sahara Desert and Roman ruins like Leptis Magna.
4.  Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to the keyword what are the 54 countries in Africa, along with concise answers:
1. What are the 54 countries in Africa?
Africa comprises 54 recognized nations, ranging from Algeria in the north to South Africa in the south. These nations are divided across five regions: North, West, Central, East, and Southern Africa.
2. How is Africa divided into regions?
Africa is divided into five main regions:
- North Africa: Countries like Egypt, Algeria, and Morocco.
- West Africa: Includes Nigeria, Ghana, and Senegal.
- Central Africa: Features countries like DRC and Cameroon.
- East Africa: Includes Kenya, Ethiopia, and Tanzania.
- Southern Africa: South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to the keyword what are the 54 countries in Africa, along with concise answers:
1. What are the 54 countries in Africa?
Africa comprises 54 recognized nations, ranging from Algeria in the north to South Africa in the south. These nations are divided across five regions: North, West, Central, East, and Southern Africa.
2. How is Africa divided into regions?
Africa is divided into five main regions:
- North Africa: Countries like Egypt, Algeria, and Morocco.
- West Africa: Includes Nigeria, Ghana, and Senegal.
- Central Africa: Features countries like DRC and Cameroon.
- East Africa: Includes Kenya, Ethiopia, and Tanzania.
- Southern Africa: South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana.
 3. Which is the largest country in Africa?
Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area, covering 2.38 million square kilometers.
4. Which is the smallest country in Africa?
Seychelles, an island nation in the Indian Ocean, is the smallest African country by both land area and population.
5. What are the most populous countries in Africa?
Nigeria leads as Africa’s most populous country, followed by Ethiopia and Egypt.
6. Which country is the youngest in Africa?
South Sudan is the youngest country in Africa, gaining independence from Sudan in 2011.
7. Are there disputed territories in Africa?
Yes, Western Sahara is a disputed territory. While claimed by Morocco, it is also recognized by some as an independent entity.
8. What languages are spoken across the 54 African countries?
Africa has over 2,000 languages, with official languages like Arabic, English, French, Portuguese, and Swahili spoken widely across various nations.
9. What is Africa's richest country by GDP?
Nigeria has the largest GDP in Africa, driven by its oil industry and diverse economy.
10. Which African country is most famous for its wildlife safaris?
Kenya and Tanzania are globally renowned for their wildlife safaris, with attractions like the Serengeti and Maasai Mara.
11. What is the significance of Africa’s Nile River?
The Nile is the world’s longest river, crucial for agriculture and life in countries like Egypt, Sudan, and Uganda.
12. Which African countries are island nations?
Island nations in Africa include Seychelles, Mauritius, Madagascar, Cape Verde, and São Tomé and Príncipe.
13. Which country in Africa has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites?
South Africa and Ethiopia boast numerous UNESCO World Heritage Sites, reflecting their rich cultural and natural heritage.
14. What are some ancient civilizations found in Africa?
Notable ancient civilizations include the Egyptians in North Africa, the Kingdom of Axum in Ethiopia, and the Mali Empire in West Africa.
15. How can I explore Africa’s 54 countries?
Africa can be explored regionally, starting with iconic landmarks like the Pyramids of Egypt, Victoria Falls in Zimbabwe/Zambia, and the Sahara Desert spanning several countries.
3. Which is the largest country in Africa?
Algeria is the largest country in Africa by land area, covering 2.38 million square kilometers.
4. Which is the smallest country in Africa?
Seychelles, an island nation in the Indian Ocean, is the smallest African country by both land area and population.
5. What are the most populous countries in Africa?
Nigeria leads as Africa’s most populous country, followed by Ethiopia and Egypt.
6. Which country is the youngest in Africa?
South Sudan is the youngest country in Africa, gaining independence from Sudan in 2011.
7. Are there disputed territories in Africa?
Yes, Western Sahara is a disputed territory. While claimed by Morocco, it is also recognized by some as an independent entity.
8. What languages are spoken across the 54 African countries?
Africa has over 2,000 languages, with official languages like Arabic, English, French, Portuguese, and Swahili spoken widely across various nations.
9. What is Africa's richest country by GDP?
Nigeria has the largest GDP in Africa, driven by its oil industry and diverse economy.
10. Which African country is most famous for its wildlife safaris?
Kenya and Tanzania are globally renowned for their wildlife safaris, with attractions like the Serengeti and Maasai Mara.
11. What is the significance of Africa’s Nile River?
The Nile is the world’s longest river, crucial for agriculture and life in countries like Egypt, Sudan, and Uganda.
12. Which African countries are island nations?
Island nations in Africa include Seychelles, Mauritius, Madagascar, Cape Verde, and São Tomé and Príncipe.
13. Which country in Africa has the most UNESCO World Heritage Sites?
South Africa and Ethiopia boast numerous UNESCO World Heritage Sites, reflecting their rich cultural and natural heritage.
14. What are some ancient civilizations found in Africa?
Notable ancient civilizations include the Egyptians in North Africa, the Kingdom of Axum in Ethiopia, and the Mali Empire in West Africa.
15. How can I explore Africa’s 54 countries?
Africa can be explored regionally, starting with iconic landmarks like the Pyramids of Egypt, Victoria Falls in Zimbabwe/Zambia, and the Sahara Desert spanning several countries. B. Traditional Clothing and Attire
Traditional clothing in Africa reflects cultural identity and societal roles. Different regions and ethnic groups have distinct styles, fabrics, and colors that convey social status, marital status, and cultural affiliation. For example, the brightly colored kente cloth of the Ashanti people in Ghana symbolizes wealth and prestige, while the intricate beadwork of the
B. Traditional Clothing and Attire
Traditional clothing in Africa reflects cultural identity and societal roles. Different regions and ethnic groups have distinct styles, fabrics, and colors that convey social status, marital status, and cultural affiliation. For example, the brightly colored kente cloth of the Ashanti people in Ghana symbolizes wealth and prestige, while the intricate beadwork of the 
 V. Conclusion
In conclusion, African culture is a vibrant mosaic of traditions, languages, and practices that vary across the continent while sharing unifying values. Exploring things to know about African culture reveals its intricate rituals, expressive art forms, and cohesive social structures. By embracing this diversity, we foster global connections and cultivate respect for one of the world's most culturally rich regions.
V. Conclusion
In conclusion, African culture is a vibrant mosaic of traditions, languages, and practices that vary across the continent while sharing unifying values. Exploring things to know about African culture reveals its intricate rituals, expressive art forms, and cohesive social structures. By embracing this diversity, we foster global connections and cultivate respect for one of the world's most culturally rich regions.



